Mean shift clustering of two-dimensional data
Mean shift clustering of two-dimensional data
Beijing Institute of Technology | Ming-Jian Li
The following Python code is a companion code for the course on Artificial Intelligence and Simulation Science. It functions to build a Mean-Shift clustering model, automatically estimate the optimal bandwidth from the generated data, and iteratively shift each point toward the local density peak to discover clusters and their centers without specifying the number of clusters in advance.
x1import numpy as np2import matplotlib.pyplot as plt3from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift, estimate_bandwidth4from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs5
6# 1 Generate synthetic data7centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [2, 2]]8X, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=500, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.6, random_state=42)9
10# 2 Estimate bandwidth11bandwidth = estimate_bandwidth(X, quantile=0.2, n_samples=500)12print("Estimated bandwidth:", round(bandwidth, 3))13
14# 3 Visualize raw data15plt.figure(1)16plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c='grey', s=30, alpha=0.6)17plt.title('Step 0: Raw Data')18plt.show()19
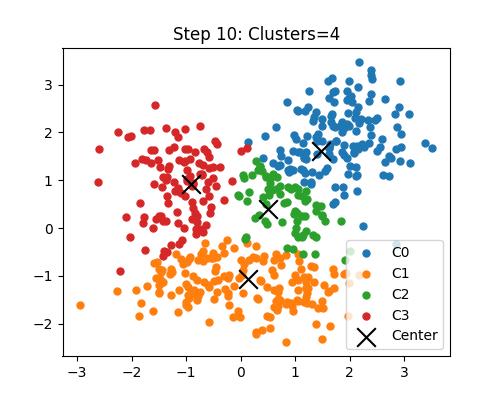
20# 4 Manually control iteration steps21max_steps = 1022for step in range(1, max_steps + 1):23 ms = MeanShift(bandwidth=bandwidth, bin_seeding=True, max_iter=step)24 ms.fit(X)25 labels = ms.labels_26 cc = ms.cluster_centers_27 n_clusters = len(np.unique(labels))28
29 plt.figure(step + 1, figsize=(5, 4))30 for k in range(n_clusters):31 plt.scatter(X[labels == k, 0], X[labels == k, 1], s=25, label=f'C{k}')32 plt.scatter(cc[:, 0], cc[:, 1], s=180, c='k', marker='x', label='Center')33 plt.title(f'Step {step}: Clusters={n_clusters}')34 plt.legend()35 plt.show()The result is: